GameTest
GameTest is an automated end-to-end (E2E) testing framework for testing aspects of Minecraft. Each test contains a structure, parameters for how the test gets executed, and optional code to further specify the test behavior.
Java Edition
Test instance
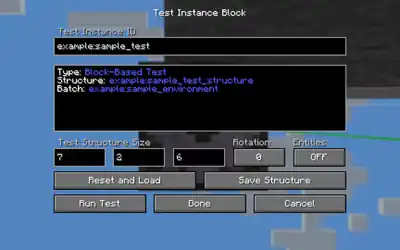
Test instance can be defined in a datapack by creating a JSON file in the test_instance registry. Players can inspect information about them using a ![]() test instance block. A test instance has the following properties:
test instance block. A test instance has the following properties:
- It belongs to a test environment, which groups the test and further specifies the environment in which the test is run in. ([NBT Compound / JSON Object][String] batch)
- It is associated with a [String] structure, which should contain all the blocks and entities it needs to be run. The structure can be easily altered with the test instance block.
- It can either be a block-based test or a function test. More information is available below.
There are more configuration available for test instances. For more information on the format, see test instance definition.
Block-based
In block-based tests, Test blocks are used inside the test structure to control the test logic using redstone signal.
 Start: A redstone pulse is triggered when the test starts.
Start: A redstone pulse is triggered when the test starts. Log: Logs a message to the log file when powered by redstone.
Log: Logs a message to the log file when powered by redstone. Fail: Fails the test when powered by redstone.
Fail: Fails the test when powered by redstone. Accept: Completes the test when powered by redstone.
Accept: Completes the test when powered by redstone.
If a race condition occurs, the first test block activated always wins.
Function
Function tests rely on built-in test functions to determine a test's success or failure. They are meant to be used by Mojang internally and by mod developers.
The game provides the GameTest framework interfaces through the net.minecraft.gametest.framework package (Mojang mapping). Mod loaders can use these to provide their own API for developers to use the GameTest framework – please refer to the respective documentation for Fabric and NeoForge for more information.
A test function must be registered in the test_function registry to be referenced in the test instance. The [String] function field in the test instance definition should contain the resource location of the test function.
Test environment
Test environment is a way to group up test instances and give them the right preconditions to run. It can be defined in a datapack by either creating a JSON file in the test_instance registry or directly specified the environment inline with the [NBT Compound / JSON Object] batch field.
Test command
The /test command exists to execute and manage block-based tests. Some notable sub-commands include:
/test (run|runmultiple) <tests> ...sub-commands can run specific test(s) for a number of times by their identifier./test (runclosest|runthat|runthese) ...sub-commands can run test(s) based on the player's location./test (resetclosest|resetthat|resetthese)sub-commands reset the test structures for any tests./test locate <tests>locates test in loaded chunks.
Server.jar entry point
The net.minecraft.gametest.Main entry point is included in server.jar which starts a server, runs all available game tests and then exits. It can be invoked in the command line, such as:
java -DbundlerMainClass="net.minecraft.gametest.Main" -jar server.jar [<options>]
Command-line options
--help- Shows usage information--packs <path>- Set a folder of datapacks to include in the world- Any zip file or folder with a
pack.mcmetafile is included
- Any zip file or folder with a
--report <path>- Exports results in a junit-like XML report at the given path--tests <selection>- Specify which tests to run with a selection - a wildcard expression matching namespace test instance IDs- If omitted, or used with an empty ID, runs all tests
--universe <path>- The path to where the test server world will be created- Any existing folder will be replaced
- Default:
gametestserver
--verify <boolean>- Enables test verification- Runs the tests specified with
testortestNamespace100 times for each 90 degree rotation step - Default:
false
- Runs the tests specified with
Exit code
The game will yield the following exit codes depending on the scenario:
| Scenario | Exit code |
|---|---|
| All tests pass | 0 |
| Any test fails | (number of failures) |
| Server shut down without starting tests | -1 |
| Game crashed | 1 |
Bedrock Edition
The GameTest framework can be accessed through the @minecraft/server-gametest module from the Script API. The module must be added as a dependency in the manifest.json. It contains many programming interfaces used for automated testing of any game objects' behaviors and interactions in a controlled testing environment, such as:[1]
- Asserting certain conditions for blocks, entities, and other game objects;
- Getting in-game information such as dimension, position, entities and blocks information;
- Modifying the testing environment by setting block permutation (block type and states data), sending redstone interactions, etc;
- Spawning entities controlled by the script with predictable mob behaviors;
- Creating simulated players for testing behaviors and interactions with other game objects;[2]
- And other testing functionalities, further reading.
A testing environment can be created from a unit test (also called a GameTest), which contains a test function registered from the script, and a reference to a .mcstructure file exists in the behavior pack.[3][4] Users can register a new unit test using GameTest#register(testClassName, testName, testFunction) method with additional builder parameters, such as .maxTicks(ticks) that indicates the test may take amount of ticks to run, .maxAttempts(attempts) which specifies how many attempt the test can run, and more.[4]
After the unit test is registered, it is loaded in the world, and can be run using the /gametest command, referenced by <testClassName>:<testName>. When ran, the game spawns the test structure and calls the test function previously defined in the script. The unit test may succeed or fail depending on the test function, which usually contain instructions for testing behaviors and interactions in the testing environment.
History
| November 9, 2020 | Henrik Kniberg demonstrated GameTest, a test framework used internally by Mojang, on the Agile with Jimmy YouTube channel. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Java Edition | |||||||
| 1.15 | 19w34a | References to GameTest added in the game's code. Most of the framework is stripped, since the rest of the game does not depend on it. | |||||
| 1.17 | 21w13a | GameTest related code is now exposed for mod developers' use because unused parts of code are no longer removed. | |||||
| 1.21.5 | 25w03a | Overhauled the GameTest framework. | |||||
| Introduced for use with data packs. | |||||||
| Bedrock Edition | |||||||
| 1.16.210 | beta 1.16.210.60 | Added GameTest framework. | |||||
References
- ↑ "Test Class" – Microsoft Learn, February 10, 2025.
- ↑ "SimulatedPlayer Class" – Microsoft Learn, February 10, 2025.
- ↑ "Building your first GameTest" – Microsoft Learn, June 20, 2024.
- ↑ a b "RegistrationBuilder Class" – Microsoft Learn, February 22, 2025.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Editions |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Development |
| ||||||
| Technical |
| ||||||
| Multiplayer | |||||||
| Exclusive features |
| ||||||
| Removed | |||||||