So as I understand it, Hawking radiation occurs when virtual antiparticle-particle pair are created near the event horizon of a black hole due to vacuum fluctuations because of Heisenberg uncertainty and one particle flies away from the black hole and the other falls in. The black hole loses mass because the one that falls in has negative energy measured by a far away observer. My question is how can a particle have negative energy in a certain reference frame? Be as techincal as possible in your answer, thank you.
Asked
Active
Viewed 252 times
1 Answers
0
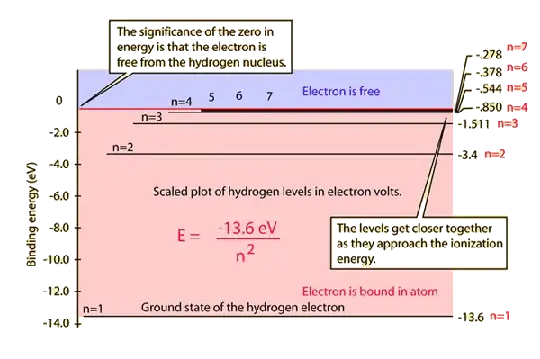
Why not negative energy? Energy is a scalar quantity that is conserved. Negative energy means that there exists a potential well which for bound quantum mechanical states has negative energy, and for free states positive. A matter of definition. Look at the hydrogen atom states
Note the - sign for the energy levels
In the case of the black hole the potential well is the gravitational well of the black hole. In an analogous way that an electron falling from 0(free state) to the first energy level it releases a photon of that energy and sticks at that level, the gravitational well will lose the analogous energy to let half of the pair to go free.
anna v
- 236,935