 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Frenapyl, Lipociden, Oberex, Vidipon, Zeisin |
| Other names | Carbamic acid, N-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylethyl]-, ethyl ester |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.659 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
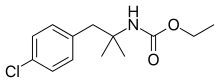
| Formula | C13H18ClNO2 |
| Molar mass | 255.74 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 89 °C (192 °F) |
| Boiling point | 52.75 °C (126.95 °F) |
| |
Cloforex (Oberex) is an anorectic of the amphetamine class.[1] It is a prodrug to chlorphentermine.[2] It never became a mass produced drug in part due to the side effects found in mice. Mice who consumed 75 mg of cloforex a day experienced weight loss along with pulmonary hypertension and hair loss.[3]
References
- ↑ Swiss Pharmaceutical Society (2000). Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory (Book with CD-ROM). Boca Raton: Medpharm Scientific Publishers. ISBN 3-88763-075-0.
- ↑ Dreyfuss J, Zimmerberg HY, Schreiber EC (1971). "Drug Metabolism.". In Cain CK (ed.). Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 6. Boston: Academic Press. pp. 205–214. doi:10.1016/S0065-7743(08)60975-6. ISBN 0-12-040506-7.
- ↑ Woodward, Stephen C. (1981). "Induction and reversal of pulmonary lipid histiocytosis in rats following oral administration of anorectics cloforex and chlorphentermine". Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health. 7 (3–4): 569–583. doi:10.1080/15287398109530002. ISSN 0098-4108. PMID 7197305.
| DRAsTooltip Dopamine releasing agents |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRAsTooltip Norepinephrine releasing agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| SRAsTooltip Serotonin releasing agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors • Adrenergics • Dopaminergics • Serotonergics • Monoamine metabolism modulators • Monoamine neurotoxins | |||||||||||||||
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.