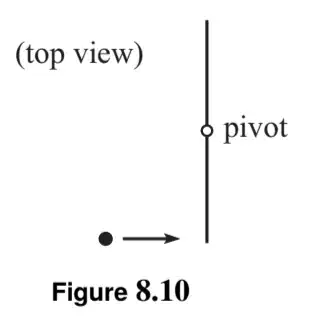
On a frictionless horizontal table, a uniform stick is pivoted at its middle, and a ball collides elastically with one end, as shown in Fig. 8.10. During the collision, what are all the quantities that are conserved in the stick-plus-ball system?
(a) L around the pivot
(b) L around the pivot, E
(c) L around the pivot, p, E
(d) L around the point of collision, E
(e) L around the point of collision, p, E
Now, when I solved this, I got answer choice $B$, which was right for what seems to be the wrong reasons. Once the stick is collided with, I thought there would be a centripetal force, meaning $p$ is not conserved. However, the component of the centripetal force orthogonal to the stick is $0$, so I thought there is no net torque around the pivot leading me to assume $L$ around the pivot is conserved. Finally, because the table is frictionless, I assumed mechanical energy is conserved.
There are probably a couple things wrong with my solution, because it fails to explain why $L$ around the point of collision is not conserved. Furthermore, the official solution seems to imply that the pivot of the stick exerts some kind of force orthogonal to the stick.
The solution:
$\boxed{b}$ There is an external force at the pivot on the stick-plus-ball system, so p isn’t conserved (the earth will gain momentum). But this force doesn’t ruin conservation of L around the pivot, because the lever arm of the force is zero, so there is no torque. E is conserved by definition, since we’re assuming the collision is elastic. Furthermore, choice (d) isn’t correct, because the force from the pivot does provide a torque around the point of collision, since the lever arm is now nonzero.
I was confused about the force at the pivot (normal to the stick) that the solution refers to. By definition, the stick is pivoted around the center, so the velocity of the center of the mass of the pivot is $0$. Does this imply that the pivot has an extremely large angular velocity to account for whatever force the pivot exerts (to keep it in place)?
I'm not quite sure where this force is coming from either, because the problem doesn't tell us whether the ball accelerates or not, so if we assume the ball to have a constant velocity, it doesn't exert any kind of force whatsoever.
Could someone explain why my solution is wrong, as well as what force the pivot exerts that the solution is referring to?