Why does vacuum particle-antiparticle creation and annihilation result in nothing rather than photons? What is the difference between that and regular annihilation that does result in photons.
1 Answers
To get an understanding on quantum field theory issues, you have to understand the difference between virtual particles and real particles.
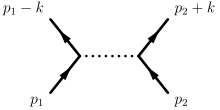
Virtual particles, in contrast to real particles, are a mathematical construct inspired by the Feynman diagrams used to describe interactions. These diagrams start with real particles, i.e. particles that have the mass and the quantum numbers of their name. In between, the mathematical formulations carry the quantum numbers of the named particle, but not the mass, because they are off mass shell.
One particle exchange scattering diagram
In the diagram above the dark lines are input and output real particles, on mass shell. The exchanged particle is virtual.
Now in quantum field theory the vacuum has fluctuations that can be defined mathematically as virtual particles continuously appearing and and disappearing within the bounds given by the Heisenberg uncertainty.
Why does vacuum particle-antiparticle creation and annihilation result in nothing rather than photons?
There is no energy to get the particles in the virtual loop to become real.
What is the difference between that and regular annihilation that does result in photons.
The vacuum "particle antiparticle" creation are diagrams involving only virtual particles. For the virtual particle antiparticle loop of the vacuum to have one particle become real it has to take energy from an interaction with a field, as happens in hawking radiation, interacting with the field of the black hole.
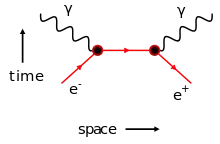
Real particle annihilation happens when the particle antiparticle are on mass shell and their energy contributes to the photons ( or other particles ) generated.
electron positron annihilation
- 236,935