You can assume either electric or magnetic field for simplicity, they both are present in light as it's electromagnetic wave.
Now, mode is a sustainable pattern in the fiber optic cable. Imagine waves on a string, only the integral multiples of half wavelengths effectively form a mode.
Let there be a complex output pattern at the output of a string. It turns out if we aren't playing with it continuously, it will be essentially periodic, maybe long period.
And we can always reduce it via fourier transforms to a sum of some basic modes.
Imagine the output at the end of a MMF(multi mode fiber) as waves on a string with intensity output as the wave amplitude on the string. It may be complex. But you can simplify the output by considering it as a sum of several modes.
You can play with waves on a string here. It won't do a fourier transform though.
http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/wave-on-a-string/wave-on-a-string_en.html
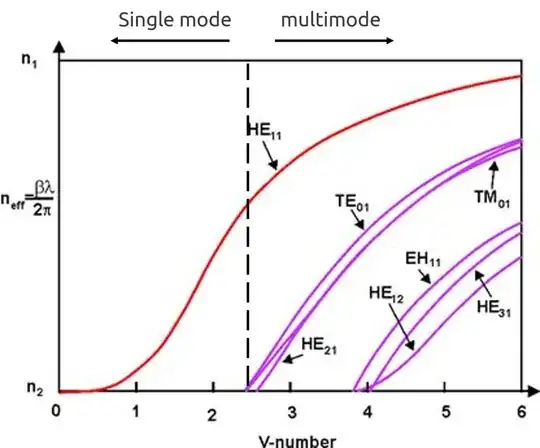
The concept is a little different for SMF and MMF.
In case of SMF, Ray theory fails and light propagates as a wavefront as explained here:
Single-mode fibers and ray-theory of light