 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
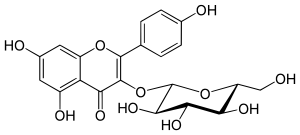
| IUPAC name
3-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
Astragaline asragalin kaempferol-3-glucoside Kaempferol 3-glucoside Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside Kaempferol-3-D-glucoside Kaempferol-3-beta-monoglucoside Kaempferol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 100568 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.128.596 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H20O11 | |
| Molar mass | 448.37 g/mol |
| Density | 1.791 g/mL |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Astragalin is a chemical compound. It can be isolated from Phytolacca americana (the American pokeweed) or in the methanolic extract of fronds of the fern Phegopteris connectilis.[1] It is also found in wine.
Astragalin is a 3-O-glucoside of kaempferol.
References
- ↑ Phenolic constituents of the fernPhegopteris connectilis. Klaus-Peter Adam, Phytochemistry, Volume 52, Issue 5, November 1999, Pages 929–934, doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00326-X
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.