 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
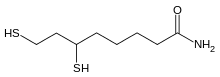
| Preferred IUPAC name
6,8-Bis(sulfanyl)octanamide[1] | |
| Other names
6,8-Dimercaptooctanamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | dihydrolipoamide |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H17NOS2 | |
| Molar mass | 207.35 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Dihydrolipoamide is a molecule oxidized by dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase in order to produce lipoamide. Lipoamide is subsequently used as a cofactor for α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, and branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex.
See also
References
- ↑ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 697. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
The prefixes 'mercapto' (–SH), and 'hydroseleno' or selenyl (–SeH), etc. are no longer recommended.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.