 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
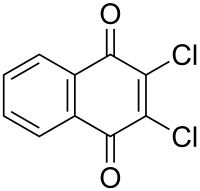
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,3-Dichloronaphthalene-1,4-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.828 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H4Cl2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 227.04 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow crystals[1] |
| Melting point | 193 °C (379 °F; 466 K)[1] |
| 0.1 ppm[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Dichlone (trade names Phygon and Quintar) is a fungicide and algicide of the quinone class. It is a general use fungicide applied to fruits, vegetables, field crops, ornamentals, and residential and commercial outdoor areas.[1] It is also used to control blue algae.[2]
Dichlone is not persistent in soil and has moderate mammalian toxicity.[2]
Dichlone can be manufactured by the chlorination and oxidation of naphthalene.[3]
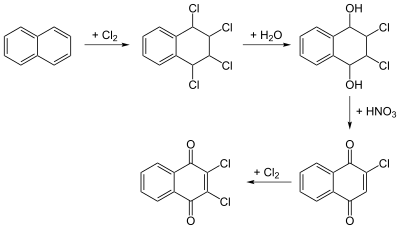 Synthesis of dichlone from naphthalene
Synthesis of dichlone from naphthalene
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Dichlone (Phygon, Quintar) Chemical Profile". Pesticide Management Education Program, Cornell Cooperative Extension.
- 1 2 "Dichlone". Pesticide Properties DataBase, University of Hertfordshire.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger (1996). Pesticide Synthesis Handbook. p. 966. ISBN 0-8155-1853-6.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.