 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
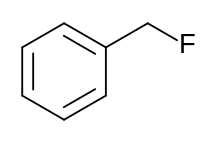
| Preferred IUPAC name
(Fluoromethyl)benzene | |
| Other names
α-Fluorotoluene, BnF | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.913 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H7F | |
| Molar mass | 110.129 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.0228 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | −35 °C (−31 °F; 238 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 140 °C (284 °F; 413 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | "External MSDS" |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Benzyl fluoride is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring substituted with a fluoromethyl group.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 90. Edition, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 2009, ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0, Section 3, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, p. 3-260.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.