 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
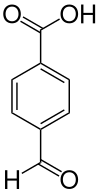
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Formylbenzoic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
4-Formylbenzenecarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.645 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 150.133 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 245 °C (473 °F; 518 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
4-Carboxybenzaldehyde (CBA) is an organic compound with the formula OCHC6H4CO2H. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with both an aldehyde and a carboxylic acid, with these functional groups on opposite corners of the ring. This compound is formed in 0.5% yield as a byproduct in the production terephthalic acid from p-xylene. Since approximately 40,000,000 tons of terephthalic acid are produced per year, CBA is a relatively large scale industrial chemical.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Barnicki, Scott D. (2012). "Synthetic Organic Chemicals". In Kent, James A. (ed.). Handbook of Industrial Chemistry and Biotechnology. Boston, MA: Springer US. pp. 307–389. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-4259-2_10. ISBN 978-1-4614-4258-5.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.