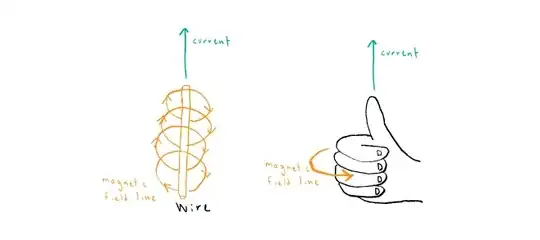
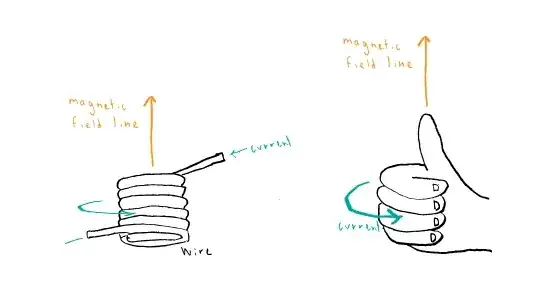
While we normally think of a current as a lot of electrical charges moving along in a wire, a single charge moving in a straight line is effectively a current, so any question involving forces between moving charges, such as this one here, directly or indirectly uses the first depicted rule.
A special case of Ampere's force law is the force between two parallel current carrying wires so that is another example.
We can reshape a single single loop of a coil as a polygon with straight sections and summing up the magnetic forces of all the straight sections would give us the total magnetic force of the loop so this is how the two rules are related.
This libretext webpage represents a single coil of an electric motor as an assembly of straight wires for easier analysis of the forces and torque produced by an electric motor as depicted in the diagram borrowed from there excellent webpage below, so any questions involving electric motors directly or indirectly use the straight current rule.