parsec is defined as the distance at which average radius of earth's orbit around sun would subtend an angle of 1''(second of arc). But suppose im looking at this star when earth is on one side of the sun, now six months later earth is on the other side of the sun and when im looking at this star theres some sort of parallax error right. Now the angle between these two observations say the angle between the line connecting the earth when it is on one side of the sun to the star and the line connected the earth when it is on the other side of the star to the sun. That's parallax right? So my baseline is the whole of the diameter of earths orbit not only the radius explain please
2 Answers
Basically... you're right. But I'll just say exactly what's going on because your question has some imprecise phrasing.
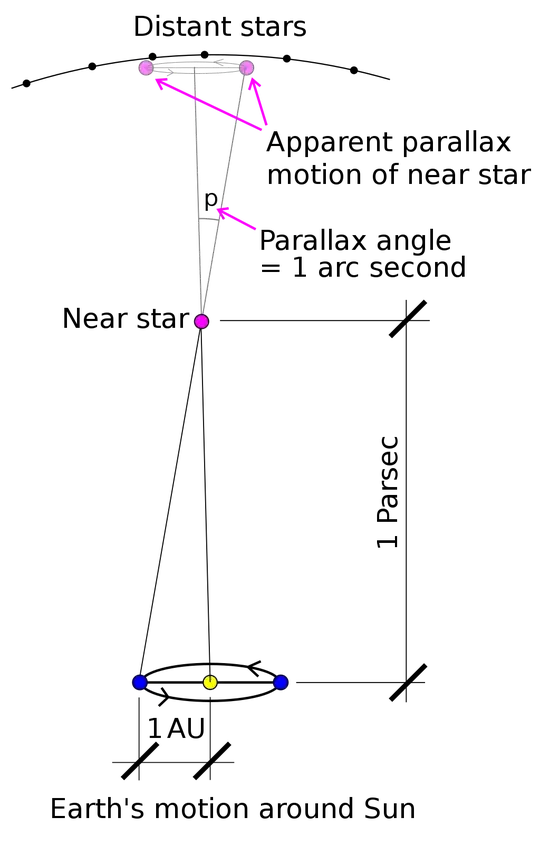
The parsec is defined as a distance such that if you change your observation position by $1\text{ AU}$ perpendicular to the direction toward a distant object, that distant object will move by 1 arc second with respect to much more distant stars. The wikipedia explains this clearly with this image:
As you point out, the earth moves by $2\text{ AU}$ in 6 months, not $1\text{ AU}$. So if a star was 1 parsec away from the earth in the direction perpendicularly up from the plane of the earth's orbit, it wouldn't move by 1 arc second in six months, it would move by two.
They could have defined the parsec either way - but they chose to define it this way. Which I support because radii are in general more convenient to work with than diameters in physics. Equations are just more often nicely written in terms of radius. Like the centripetal acceleration formula $a=v^2/r$
- 8,778
Parallax is a strictly visual phenomenon caused by the fact that we have two eyes which see faraway objects from slightly different angles. Wikipedia defines parallax as "a difference in the apparent position" (emphasis mine) of an object, which is not the same as a difference in the actual position. The distance between Earth and the Sun at any given time is defined as the difference between their centers of mass, which can be computed exactly with modern techniques without worrying about the effects of parallax. Thus, the average radius of the Earth's orbit is a perfectly good "measuring stick" that can be used to define units such as the parsec.
- 384