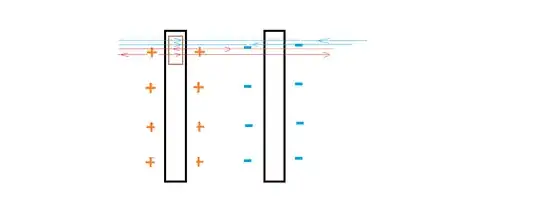
Suppose I have two metal plates in a vacuum and I give this system some electric charge,the charge would distribute itself according to Gauss law on both the inner and outer walls of both plates...but if I were to hook the plates to a battery and convert this system into a capacitor ...all the charge would be on the facing surfaces and none on the outer walls ..why is this so??
I had seen a question in Concepts of Physics by HC Vermain which a system of two plates was given and one plate was charged with +Q and they said to find the potential difference between the two plates but in applying Q=CV they considered only the facing side's charges and my teacher said that this is because in a capacitor charges only reside on the inner walls and hence we are not considering the charges on the outer walls in consideration and when we hook the capacitor to a battery there will be no charge remaining on the outer walls
What is the precise math and corresponding equations behind it? Is there any explanation based on electric field and potential?