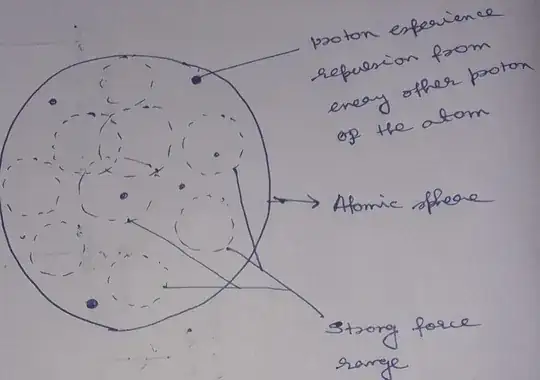
Does the strong nuclear force balance the electrostatic repulsions between the protons or does it overcome the repulsion?
I looked up on wikipedia and it says that the strong nuclear force is strongest of all the fundamental forces. Based on that i assume that it overcomes the electrostatic repulsions.
Now what if there are more protons than neutrons (or less neutrons than protons), in the nucleus? Wouldnt this mean that the electrostatic forces are stronger than the strong nuclear force?
If the electrostatic forces are stronger, what would happen to the nucleus? Would it break apart? (is it related to the stability?)
In addition to this, at what stage do we know (or by how much in the difference between protons and the neutrons) would cause the electrostatic forces greater than the strong nuclear force?
Thankyou.