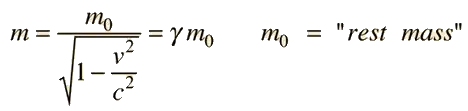I am a bit confused that what actually the Einstein's equation meant to describe binding energy wht is that $c^2$ for as when nucleon combine what is the need of speed of light in equation?
1 Answers
The equation E=mc^2 is useful when it relates energy and mass in special relativity, when m is the specific rest mass of a particle or a nucleus, i.e. the length of any four vector that would describe the particle in all Lorentz covariant frames.
c is not the velocity of the particle described by the equation. It is a constant imposed by the algebra of special relativity, a scale factor, that happens to be the velocity of light in vacuum. In particle physics one often works in computational systems where c is set equal to 1.
The general formula has m as the relativistic mass, where the velocity of a particle enters as v.
This is not useful for nuclear and particle physics, where the sums for binding energies have to use the m_0, invariant mass to Lorentz transformations.
- 236,935