Why the speed of light is said to be constant?
Because of the tautology wherein we use the motion of light to define the second and the metre, then use them to say what the speed of light is. See http://arxiv.org/abs/0705.4507 :
"Following Ellis 1, let us first consider c as the speed of the photon. Can c vary? Could such a variation be measured? As correctly pointed out by Ellis, within the current protocol for measuring time and space the answer is no. The unit of time is defined by an oscillating system or the frequency of an atomic transition, and the unit of space is defined in terms of the distance travelled by light in the unit of time. We therefore have a situation akin to saying that the speed of light is “one light-year per year”, i.e. its constancy has become a tautology or a definition".
The speed of light in vacuo is not constant. See Einstein saying so here.
If we ask someone what is the speed of light, then everyone will say that it is constant and its value is $3\times 10^{8}m/s$.
Not me. I'll say it isn't constant, and that 299,792,458 m/s at one elevation is not the same as 299,792,458 m/s at another because the seconds are different.
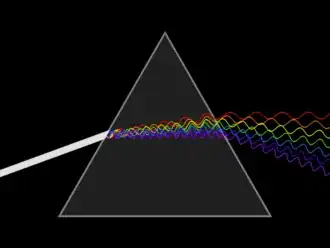
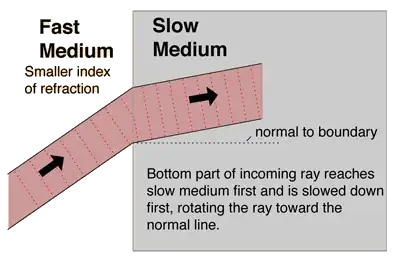
But if we recall our mind about refraction of light. we says that when the light travel from a rarer medium to a denser medium then its speed become slow. See the Image first. But still its speed is constant. WHY ???
Because it isn't going straight any more. The light is going at the same speed in the glass as in the air at that location, or in vacuum at that location. It's still travelling at c, but it isn't propagating in a straight line. Instead it's bending back and forth as it passes the atoms. For an analogy, imagine you can walk along a pavement at 4mph. When the pavement is empty, it takes you an hour to travel four miles. But when the pavement is crowded, you're dodging around people. You're still walking at 4mph, but it takes you an hour and a half to travel the four miles. Note too that if you're a little old lady with short little steps walking at 4mph, you're held up more than if you're a big guy with long strides walking at 4mph. In similar vein short-wavelength blue light is held up more than long-wavelength red light. So it refracts more. The effective speed or phase velocity is less. But both the blue and red light are still propagating at c.