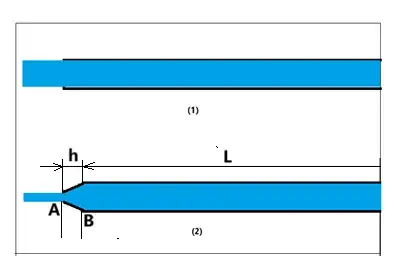
According to the Bernoulli's equation, if velocity decreases, then pressure increases.
I am trying to understand the Bernoulli's effect based on a situation.
Suppose we have a stream of water. Let's assume it is an ideal fluid. Imagine the water flows out from a wider pipe to a narrower pipe. Since the area decreases, according to the Continuity equation, velocity of water molecules increase. This causes an decrease in pressure.
I don't understand the last part. If water molecules' velocity increase, then their kinetic energy also increases. Wouldn't this causes more collision between pipe's wall and water molecules, thus giving higher pressure?