My question is about a toy hovercraft - a balloon connected to a CD. I need to know about something. How does cross section of the pipe affect the time that the toy hovercraft hovers above the surface?
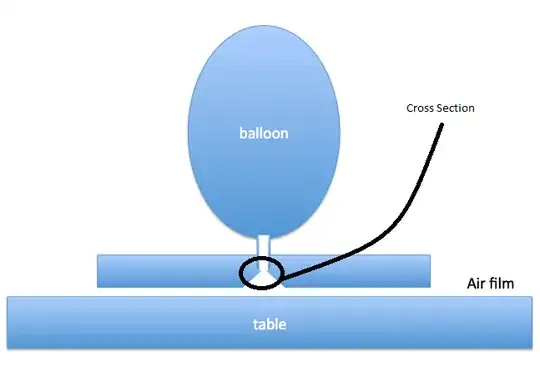
My question is about a toy hovercraft - a balloon connected to a CD. I need to know about something. How does cross section of the pipe affect the time that the toy hovercraft hovers above the surface?

The exact answer to your question can be found at http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/ppois2.html#tub
There it shows that the flow rate goes as the 4th power of the radius of a pipe - so if you double the diameter, air will flow 16x faster.
The reason behind this is something I described in some detail in this earlier answer.