I'm looking to make extra payments to my student loans. I currently owe $30,000 at 5.25%. I pay $250 on the 15th of every month. My loans accrue interest daily that are then compounded monthly. I want a formula that will show the effect of paying my loan down daily ($5), weekly ($35) or bi-weekly ($75).
3 Answers
There is no single formula that will do this comparison for you. There are formulas that will help you get there, but there's no =comparepaymentstrategy(strategyA, strategyB).
Separately, paying X per month vs X divided by 2 twice per month is an extremely incremental difference.
Lets say you have your $30,000 loan at 5.25%. Fully amortized over 15 years that's a payment of $245.44, almost the $250 you're paying now. The daily interest on $30,000 is about $4.31, the daily interest on $29,925 (an extra $75 payment that is applied directly to principle) is $4.30. So you'll save something around $0.01 per day between payments when paying multiple times in a month versus simply loading all your expected payments into your monthly amount. Generously assuming $0.01 of savings every single day over 15 years is a total of about $657 or about $44 per year. This is a generous assumption because the regular principle will exist every month until you make your mid month payment(s), you can never have a full month of savings. All of this assumes your lender will take multiple payments each month and apply them directly to the principle, which is unlikely.
There isn't much compounded benefit, because the incremental savings is so low. $30,000 (regular principle) vs $29,925 (principle less mid month partial payment) vs $29,924.85 (less the interest saved from the prior month's mid month payment). You're removing $0.15 or so from the principle each month because either way the same total amount is being paid each month. It would be several months before that savings grows to a point that it becomes more than a rounding error at 5.25% annual interest which would generate a compounded savings..
- 49,074
- 11
- 101
- 161
look at function cumipmt (I think that's the right name) First, get the function to duplicate your existing loan and make sure you get it to match reality. Then you can add extra payments in
CUMIPMT(rate, nper, pv, start_period, end_period, type)
I'm not sure how to adjust for periods different than your regular payment period.
- 1,181
- 5
- 6
I'm sure there is no built-in Excel formula for the OP's calculation, but one can be constructed like so: Considering case for $250 monthly plus $5 daily:
Taking into account monthly compounding of the nominal rate,
the monthly rate r = 5.25/100/12
the effective annual rate yr = (1 + r)^12 - 1
Now calculating everything on a daily interest basis with months of average length:
average number of days per year dy = 365.2425
average days per month av = dy/12
daily rate dr = (1 + yr)^(1/dy) - 1
principal s = 30000
The payments:
d1 = 5
d2 = 250
The program, or formula:
p[0] = s
n = 0
While[p[n] > 0,
p[n + 1] = p[n]*(1 + dr) - d1 - If[Floor[Mod[n, av] + 1.063] == 30, d2, 0];
n++]
With $5 paid daily the loan is paid down in 2,770 days, or 2770/av = 91 months.
With d1 = 0 the loan is paid down in 5,205 days, or 5205/av = 171 months.
Check: using the standard formula for time to repayment with $250 monthly:
months = -(Log[1 - (r s)/d2]/Log[1 + r]) = 170.53, so 171 months to complete.
Explanatory note:
Floor[Mod[n, av] + 1.063] == 30 is true once at the end of every average month, i.e. at n = 30, 61, 91, 122 etc. so it applies the $250 repayment at the end of each average month.
This could be quite readily transcribed to an Excel formula. I will see about adding variations for weekly and bi-weekly.
Addendum
Adding extended formula for daily, weekly, bi-weekly and monthly
(* Setup rate constants *)
r = 5.25/100/12;
yr = (1 + r)^12 - 1;
dy = 365.2425;
av = dy/12;
dr = (1 + yr)^(1/dy) - 1;
s = 30000;
p[0] = s;
n = 0;
(* Set repayment amounts *)
d1 = 5;
d2 = 35;
d3 = 75;
d4 = 250;
(* Run formula *)
While[p[n] > 0, p[n + 1] =
p[n]*(1 + dr)
- d1
- If[Mod[n + 1, 7] == 0, d2, 0]
- If[Mod[n + 1, 14] == 0, d3, 0]
- If[Floor[Mod[n, av] + 1.063] == 30, d4, 0];
n++]
Results
daily weekly bi-weekly monthly days to pay-down months
d1 d2 d3 d4 n n/av
0 0 0 250 5205 171
5 0 0 250 2770 91
0 35 0 250 2770 91
0 0 75 250 2678 88
5 35 75 250 1414 46.5
Adding $5 daily or $35 weekly result in the same loan period reduction.
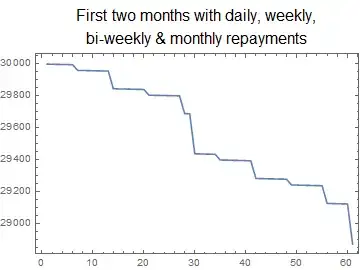
The case will all repayments is added for interest. This is how it looks graphically:
For an Excel implementation this is the first idea for transcription:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4939537/how-to-loop-in-excel-without-vba-or-macros
- 10,107
- 1
- 21
- 36