I am under the impression that declines in the stock market are more sudden and violent than increases. Is there any truth to it? If so, what causes stock prices to fall faster than they rise? Or could this all be an illusion caused by the pain of loss (loss aversion)?
10 Answers
Generally yes, as can be readily seen from looking at graphs of market indices.
I don't think anyone can say with absolute certainty what the reason is, but a good bet is that it's largely due to panic selling. Most people don't seem to be able to hold on during a drop: they want to sell NOW to limit loss, which makes the drop greater, which increases the selling pressure. This continues until everone who panics has sold.
But for increases, there's generally no such pressure to immediately buy. (Outside of rare cases like the recent GameStop thing.) People take their time getting back in (and may not have as much money to get back in with, because of the panic selling). If they delay, they've only lost a bit of hypothetical profit.
- 11,182
- 1
- 30
- 40
This is closely related to the fragility of things and can easily be observed in times of war: it is much quicker and easier to destroy something than it is to build it.
Companies can easily be regulated out of business at the stroke of a pen, found to be fraudulent or run out of cash if credit dries up and so on. These can wipe out huge parts of the value of the company in a matter of hours in some cases.
There isn't really an equivalent the other way around: even amazing breakthrough technology like google still take years or even decades to fully scale out. Building things follows medium paced, incremental growth for the most part; destruction often follows fast paced, large collapses of capital, and this appears in the numbers as it happens over time.
- 5,808
- 20
- 20
I pulled the DJIA close data, by day, from 1990 to today and calculated the percent change of the market by day. For clarity, I filtered out days where the market moved less than 2% in either direction. I would conclude there are more days of big falls than big rises, but overall the data is fairly symmetric. The skewness of the percent difference is -.16, which tells us that the left tail of the distribution (drops in the market) is a bit fatter than the right tail (rises) (when compared to a normal distribution), but not significantly so. Usually we don't consider a distribution to be moderately skewed until the skewness is either < -.5 or > .5 . The histogram and density plots tell a similar story:
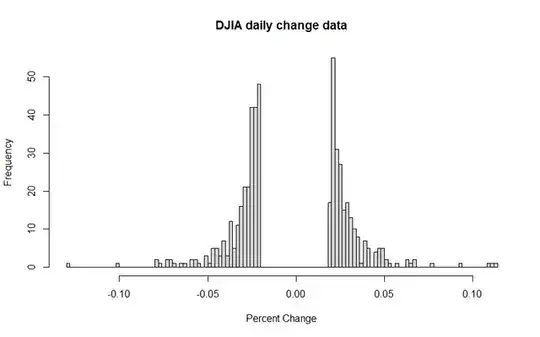
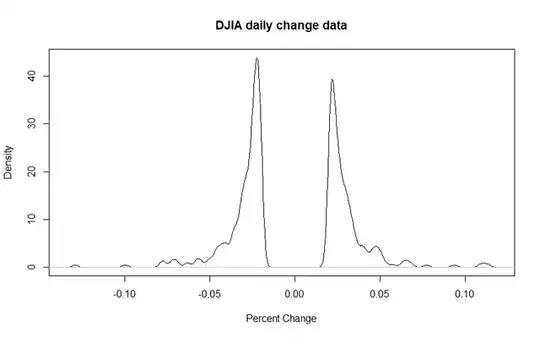
- 1,343
- 8
- 14
During normal trading, the size of rallies and pullbacks are somewhat equal. For Black Swan events, it falls much faster than it rises.
From March 9, 2003 to October 16, 2007, a period of 1682 trading days, SPY rallied from $63.85 to $131.31, a gain of 106%. From October 16, 2007 to March 9, 2009, a period of just 510 trading days, SPY gave all of those gains back, and then some, falling to $59.90. Thus, it took SPY 1682 days to gain 67 points, but just 510--or less than one-third the time--to lose the same amount.
Fast-forwarding 2 years, Figure 2 below shows SPY from October 3, 2010 to October 3, 2011 during the period of the European Crisis. These two charts suggest anecdotally that the market does appear to fall much more quickly than it goes up.
During periods of increased volatility, SPY does indeed decline at a faster rate than it rallies. The top 5% of 90-day rallies was at 18.4% while the bottom 5% of 90-day declines was at -26.6%, a decline:advance ratio of 1.44.
In the last 50 years, the most pronounced fall of the S&P in one day was 20.5%, on the contrary, the largest increase, just 11.6%. Fear motivates people more than greed.
- 77,328
- 15
- 101
- 175
The evidence certainly seems to show that it falls much quicker than it rises. My opinion is that the quick falls are because people (some from panic and others through planning*) try to "get out now while the gettin's good".
* Stop-loss orders, for example.
- 50,786
- 10
- 107
- 170
When bubbles burst, yes
When the stock market fallings makes headlines, yes. The crash is much faster than the recovery - because the market was inflated to begin with. A Random Walk Down Wall Street covers several of these crashes in great detail.
Over the long run, the total value of the stock market is slowly going up, which is also covered in the book. Because of this, over the long-term the market is always rising slightly faster than it falls, but that doesn't make headlines.
You only know it's a bubble when it burst
NOTE: This is all covered in the book
No one can accurately predict when a bubble starts. Right up to the epic crash, millions will believe the bubbled asset is undervalued. The crash always starts the same way.
A few big investors sell off a good portion of their holdings at sky-high values. Onlookers see this as a smart move - cashing out while the market is hot. A few more smart investors sell their stake to a horde of willing buyers. More onlookers see people unloading, and follow the trend. Each round floods the market with shares, driving the prices further down.
Soon investors want to "get out while they can", and flood the market with even more lower priced shares. Soon there are far more sellers than buyers. Value is based on supply and demand. Supply vastly outstrips demand in this case.
This generally happens in no more than a few days. Suddenly companies that were propped up by shady accounting practices and sky-high valuations that no longer exists collapse (see Enron). This drives the market even further down, and exacerbates the existing investor panic.
In a few months everyone agrees the assets was hugely over-valued, and promises to be more disciplined in the future.
Why?
I personally blame The Dunning-Kruger Effect - Incompetent people can't tell just how incompetent they are. Never underestimate the power of stupid people.
- 4,109
- 1
- 18
- 22
Another factor that hasn't been mentioned so far, is the use of stop-loss orders and margin-calls. Both of these cause automatic liquidation of the holdings when there is a sudden drop in the stock price, which itself reduces further the stock price, in a self-fueled cycle.
The same is not generally true for upward movements, as usually there is no automatic buying of stocks when the price goes up. The rare exception is when there are short squeezes.
- 280
- 1
- 6
An important thing to understand is that the market price of a stock is merely an estimate of the amount of money one would have to spend per share to acquire a non-trivial number of shares, or the amount of money one would receive per share to sell a non-trivial number of shares. If at some moment in time there's someone who wants to buy 10 shares and is willing to pay $100 apiece, buy nobody else who would be willing to pay more than $0.10/share, then someone who sold 100 shares just then would receive $100 for each of them. If the person waited until 50 shares had been sold to the $100 buyer, the person would only receive $100 for 50 shares and $0.10 for the other 50, thus only receiving an average of $50.05 for them, but the market price prior to that 100-share transaction would still have been $100, since all active trades would have been occurring at that price. If the person waited until 99 shares had been sold, then only one share would sell at $100 and the other 99 at $0.10, for an average price of just under $1.10, but the as before market price before the 100-share transaction would have been $100.
As soon as anyone tries to sell more shares than anyone was willing to buy at a price over $0.10, the market price will fall instantly to $0.10/share, but the decline in the amount of money one would be able to receive for 100 shares would not have fallen instantly. Instead, the attempt to sell the 101st share will reveal to everyone that the the maximum price for which one could hope to instantly sell 100 shares was nowhere near the $100/share previously thought, but was in reality at most $0.10/share. While it may seem as though the value of a 100-share holding had dropped instantly from $10,000 to $10, in reality the liquidation value will have steadily declined from $10,000 to $10 as people sold shares to the person who was paying $100 each for them; the notion that the shares had continued to be worth $10,000 until the 101st share was sold is an illusion.
- 878
- 6
- 5
Yes, falls are observably steeper than rises for the market as a whole.
I think that they main factor here is linkage - both real and imputed - between the value of stock in different companies.
Linkage between stocks in the same sector is rational enough. Even if paper companies A, B, C and D on the Finnish stock market have somewhat different business models and different calibre managements, what's good for one is often assumed to benefit others in that sector. Likewise with companies supplying raw materials or component parts to a successful company and companies that are its customers as these may be read to be the prime drivers for their growth.
Excitement rather than analysis can drive further stock buying even though linkage to the successful companies become more tenuous. With so much dependent on the fortunes of the successful companies, a small disappointment in their quarterly projections can have huge impact on the expectations of those stocks piggybacking on them. This leads to a rush to sell - a process accentuated by short sellers seeing an opportunity to cash in on a falling market. Result - a significant drop to numerous stock prices and therefore to the market as a whole.
Huge drops in stock indices can be down to fundamental economic problems being exposed, e.g. sub-prime mortgage fiasco, or to a freak event affecting a major set of players, e.g. the Kobe earthquake's financial after-shock. These drops are very steep.
Rises in the stock market are usually much more gradual over a period of time as investors try to rationalize their buying to the growth in a company's performance. Exceptions occur when a new oil/gold field is found and other companies drilling nearby are expected to bring one in also. Indeed the entire local economy might be expected to benefit as would companies providing a variety of functional and leisureful services to the local population.
- 109
- 5
Does the stock market fall faster than it rises?
Sure, this is an absolute basic in trading.
stock market
It seems to apply to ALL markets traded by humans.
(This was first observed by Homma, "God of the markets" (1700s era) who more or less invented much of what we think about "trading", particularly what we would not think of as "day trading" or "chartism".)
I am under the impression that declines in the stock market are more sudden and violent than increases.
sudden and violent are meaningless
in a general sense, I personally don't find them to be "sudden and violent" at all. It's just that markets go down faster than they go up.
Is there any truth to it?
Yes, it's the most basic principle of markets and trading.
(Note that indeed, for this very reason, many badass traders will indeed only trade downwards. Why bother with the slow direction? Any salty old trader that tells you about some huge win they had, it's usually picking a top or jumping on a down leg.)
If so, what causes stock prices to fall faster than they rise?
This is absolutely unknowable, and it's "strange that you asked" so to speak. Nobody has a clue about such mass-human-behavior qualities.
(To me it would be "obvious" that they would "go up faster" - in general terms due to "human greed and stupidity". Humans tend to "hang on to losers" and "stick with bad decisions" - you know? So any guesses you hear are just guesses.)
Or could this all be an illusion caused by the pain of loss (loss aversion)?
No, it's an extremely well-known, obvious, agreed-upon observation on the nature of human markets.
- 13,940
- 4
- 34
- 60