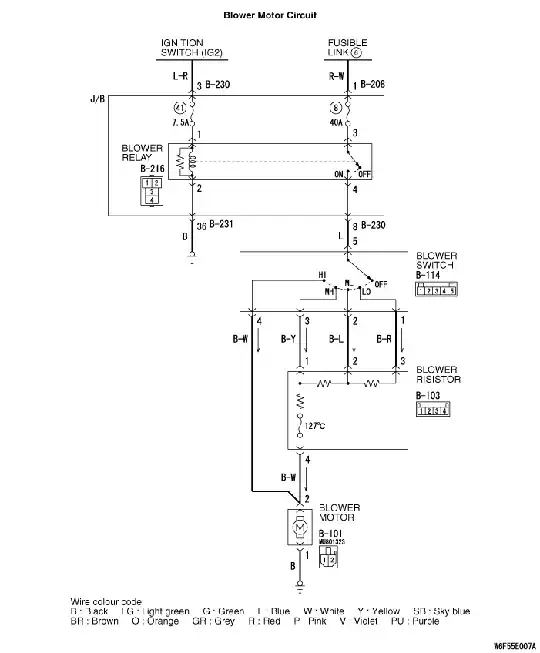
Q - why is the circuit described below protected with a 40amp fuse when the cable to the motor is 2mm² (I cut a bit of cable out and measured strand thickness and quantity, 37 * .26mm = 1.98mm²) and therefore likely rated for 25amps max. (All the vehicle wiring shops, that I've looked at, list 2mm² thin wall cable as rated for approx 25amp max.)
Am I misunderstanding something about the max rating?
Background to question - I was planning on wiring the motor direct as there is a fault somewhere (tested motor, relay, fuse and resistor pack and they are all good) and I don't want to pull apart dash to find offending wiring but this has stumped me as I assumed I'd need 6mm² cable to match the 40amp fuse but manufacturer uses only 2mm².
I guess the motor may well be drawing considerably less amps (not tested) but then the question still remains why use a 40amp fuse.
Thanks in advance.