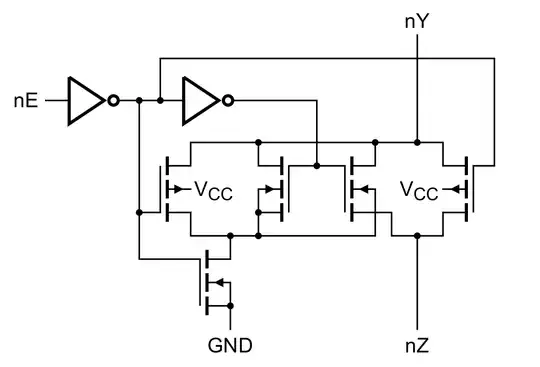
The following is the logic diagram of a single pole double throw analog switch that I am trying to use.
Specifically what I am wondering is if it connects one of nY or nZ to ground when nE is low.
But I also have no real clue on how to interpret this in general. Specifically the center connections to the mosfets have me confused as I have never seen that before and I do not know which terms to search for to find out what they are doing.
For context, the diagram is from this chip: https://assets.nexperia.com/documents/data-sheet/74LV4066.pdf