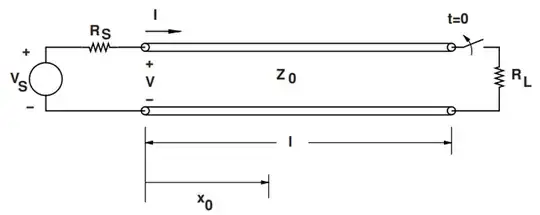
Some background information:
I have a transmission line circuit (included below). The rated voltage is 63.639kV and the rated current is 325A. The characteristic impedance is 30.3 Ohms. I also have inductance, capacitance, and speed. The line is fifty kilometers long.
After the switch is opened, disconnecting the receiving end from the sending end, the voltage at the receiving end is 73kV and the current from the sending end is 325A. After 272us (T), the voltage at the receiving end doesn't change, but the current is now -325A. After 544us (2T), the voltage at the receiving end is 53kV, and the current at the sending end is still -325A.
Why does the voltage increase when the circuit is opened, but then decrease after 544us but not after 272us?
Why does the current change from 325A to -325A after 272us and not immediately after the switch is opened?
What is the relationship between voltage and time?
What is the relationship between current and time?