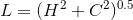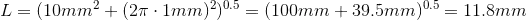Sometimes we might need to know the exact length of the wire pairs inside a cable. One can be interested in calculating voltage drop or some other calculation regarding the exact length.
Because the wires inside the cable are twisted, their actual(electrical) length is greater than the cable jacket length.
Is there any practical method to calculate the actual length?
I couldn't find a duplicate, but if there is I will delete this question.