Analyzing the charge and discharge curve characteristics is the most reliable but also the most time consuming.
Measuring the internal resistance of an Li-ion offers little value as Li-ion keep a low and consistent resistance throughout their life cycle. It may identify the cells that have little or no life left.
Measuring the impedance curve between 1hz and 10hz is a reliable quick method but a bit complex.
A 3.7V, 18650 cell is an Li-manganese which is used in power tools because it can withstand short heavy discharge rates. Some cells can withstand up to a 5 second 30C discharge. This lends itself to testing its capacity by measuring the electrochemical dynamic response with the Pulse Discharge Test method. This measures the ion flow between the positive and negative plates.
The Pulse-Discharge method is the quick and somewhat simple method.
It is important the cell not be fully charged and ideally at about a 40% charge level.
A resistive load with between .1C and 2C discharge is applied for between 1 and 6 seconds, not to exceed 6 seconds.
A strong cell recovers quickly, weaker cells are slower getting back to the pre-pulse voltage.
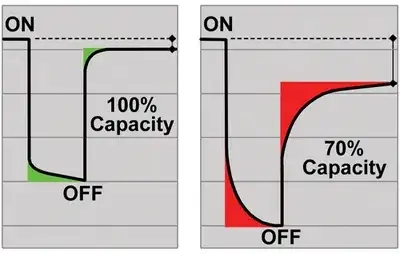
- Measure voltage before discharge pulse.
- Measure discharge voltage within one second after falling edge.
- Measure open circuit recovery voltage within one second after the
rising edge.
This is a patented process Patent Number 7,622,929
The patent has much more detailed information.

