The rectifier diode and the Zener diode are both types of semiconductor diodes, but they serve different functions in electronic circuits.
Rectifier Diode
Function: Rectifier diodes are primarily used for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) in power supply applications. They allow current to flow in one direction only, essentially rectifying the AC signal.
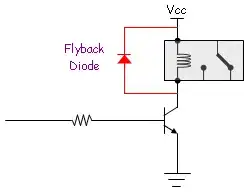
Forward-Bias Operation: In a forward-biased state, a rectifier diode conducts current easily, allowing current to flow from the anode to the cathode.
Reverse-Bias Operation: In a reverse-biased state, a rectifier diode blocks the flow of current, acting as an open circuit.
Zener Diode
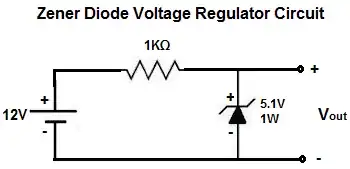
Function: Zener diodes are designed to operate in the reverse breakdown region, maintaining a constant voltage across their terminals. They are often used for voltage regulation and voltage reference in electronic circuits.
Reverse-Bias Operation: Zener diodes are used in their reverse-biased state, and when the voltage across them exceeds a specific value (the Zener voltage or breakdown voltage), they start conducting in the reverse direction.
Voltage Regulation: Zener diodes provide a stable voltage output, making them suitable for applications where a constant voltage is required.
Differences
Operating Region: The key difference lies in the operating region. Rectifier diodes operate in the forward-biased state for rectifying AC signals, while Zener diodes operate in the reverse-biased breakdown region for voltage regulation.
Functionality: Rectifier diodes convert AC to DC, whereas Zener diodes regulate voltage by maintaining a constant voltage drop across their terminals.
Breakdown: Rectifier diodes are not designed for intentional breakdown, while Zener diodes are specifically designed to operate in the breakdown region.
You can find more information about the differences between the Zener diode and rectifier diode in this post: https://medium.com/@chris_53665/differences-between-zener-diode-and-rectifier-diode-413208e9bbf0