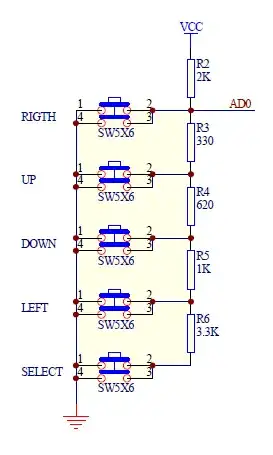
You can make a voltage divider with any number of resistors, but you must remember that any current drawn from an output of a voltage divider must come through the resistors in that divider, so will affect the output voltage.
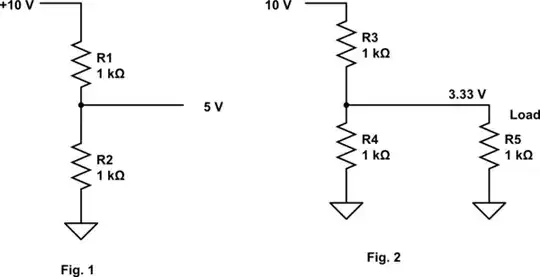
simulate this circuit – Schematic created using CircuitLab
In Fig. 1, we have a simple voltage divider. Since the resistors are equal value, the output voltage will be half the input voltage (10V in gives 5V out).
However, in Fig 2 we've added a load (R5) intended to draw 5 mA from the voltage divider. However, that load is in parallel with R4, so we effectively have a 1K resistor (R3) in series with a 500 ohm resistor (R4 and R5 in parallel), so we only get 3.33 volts for our load, rather than the desired 5 volts.
When designing a voltage divider you must always make allowance for any currrent drawn from a tap on the divider, usually by ensuring that the current drawn by the load is much less than the current through the divider chain.