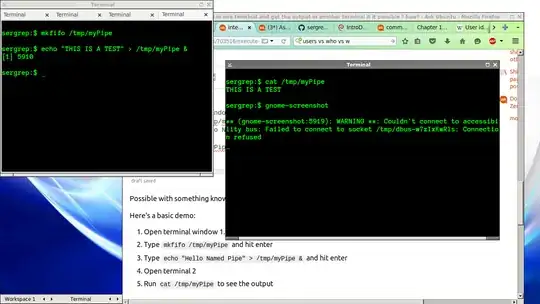
Execute command in one terminal and get the output in another terminal
2 Answers
Possible with something known as named pipe.
Here's a basic demo:
- Open terminal window 1.
- Type
mkfifo /tmp/myPipeand hit enter - Type
echo "Hello Named Pipe" > /tmp/myPipe &and hit enter - Open terminal 2
- Run
cat /tmp/myPipeto see the output
Another possible solution is to have a screen session running, and attach/detach to it.
- 107,582
On the receiving terminal, execute the command w. This will print a list of currently running sessions, e.g. when I run the command, it prints:
13:39:22 up 11 min, 3 users, load average: 0.32, 0.50, 0.33
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
sebastia tty8 :0 13:27 11:52 21.10s 0.31s cinnamon-session --session cinnamon
sebastia pts/1 :0 13:36 10.00s 23.90s 0.29s sudo apt-get update
sebastia pts/3 :0 13:37 1.00s 0.11s 0.01s w
The one you're in is of course the one with the command w (Listed in the column WHAT).
In this list, you'll also find a section called TTY. There you will see the name of the terminal buffer file, e.g. pts/3 for the one I executed w in.
Now let's assume I want to execute the command running in pts1 to print its output to pts3. This can be done like this (using the command from above):
sudo apt-get update > /dev/pts/3
This will forward all output to pts3. However, it will not take any input from there. Unfortunately, I didn't manage to find a solution for this. (Additions welcome)
Depending on what you are trying to achieve, a terminal multiplexer, such as Tmux or GNU Screen may be better suited for this task. e.g. with Tmux, proceed as follows:
Start Tmux with the command tmux. You'll be dropped to a new shell. Execute your command there.
In the receiving terminal, run tmux a to attach to the existing Tmux session. You can now interact with this terminal.
If you wish to do so, you can detach from Tmux anytime with Ctrl+B, followed by D. You can reattach from anywhere with tmux a.
- 14,644
- 12
- 60
- 83