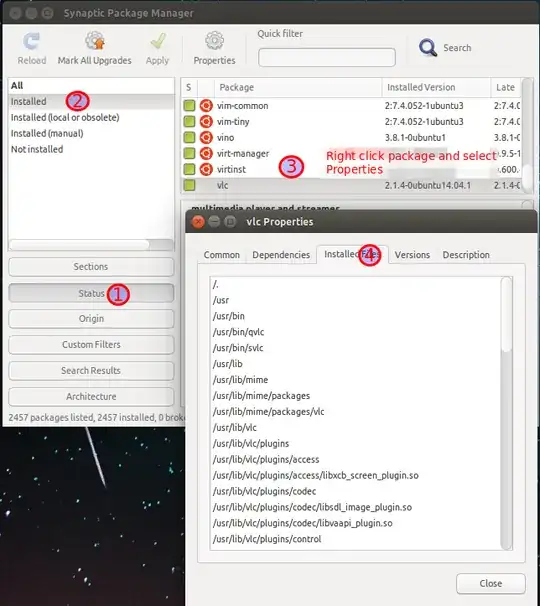
This is another way where it doesn't matter whether the package is already installed or not.
install the apt-file helper package
apt install apt-file
then run the apt-file list command
example (here for a python package installed from the repository):
apt-file list virtualenvwrapper
Result
virtualenvwrapper: /etc/bash_completion.d/virtualenvwrapper
virtualenvwrapper: /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/virtualenvwrapper-4.3.1-nspkg.pth
virtualenvwrapper: /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/virtualenvwrapper-4.3.1.egg-info/PKG-INFO
virtualenvwrapper: /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/virtualenvwrapper-4.3.1.egg-info/SOURCES.txt
etc etc etc
virtualenvwrapper: /usr/share/doc/virtualenvwrapper/html/search.html
virtualenvwrapper: /usr/share/doc/virtualenvwrapper/html/searchindex.js
virtualenvwrapper: /usr/share/doc/virtualenvwrapper/html/tips.html
virtualenvwrapper: /usr/share/python/ns/virtualenvwrapper
virtualenvwrapper: /usr/share/virtualenvwrapper/virtualenvwrapper.sh
virtualenvwrapper: /usr/share/virtualenvwrapper/virtualenvwrapper_lazy.sh
More about apt-file:
apt show apt-file
Package: apt-file
Version: 3.1.5
Priority: optional
Section: universe/admin
Origin: Ubuntu
Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <ubuntu-devel-discuss@lists.ubuntu.com>
Original-Maintainer: APT Development Team <deity@lists.debian.org>
Bugs: https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+filebug
Installed-Size: 84.0 kB
Depends: perl:any, apt (>= 1.3~exp1~), libapt-pkg-perl, liblist-moreutils-perl, libregexp-assemble-perl
Breaks: apt-venv (<< 1.0.0-1~), command-not-found (<< 0.2.38-2~), devscripts (<< 2.15.10~)
Download-Size: 25.5 kB
APT-Manual-Installed: yes
APT-Sources: http://de2.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic/universe amd64 Packages
Description: search for files within Debian packages (command-line interface)
apt-file is a command line tool for searching files contained in packages
for the APT packaging system. You can search in which package a file is
included or list the contents of a package without installing or fetching it.