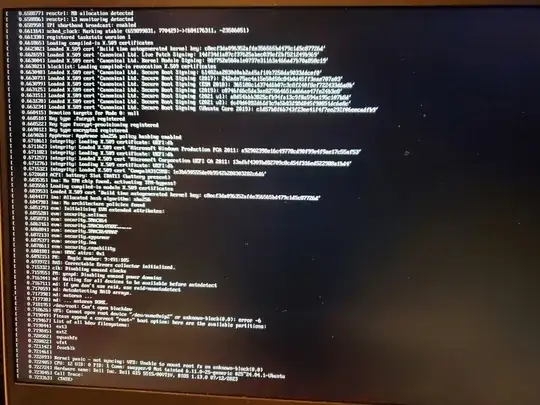
Laptop wont boot after driver update
I use a Dell G15 Ryzen edition that i flashed to ubuntu. it currently uses Ubuntu 24.04, and in the process of updating drivers to fix an issue where i couldnt connect a display through hdmi, I screwed up my computer.
I think what went wrong was when I tried doing multiple different driver updates, updating the same driver to different things, all at once before resetting, and now it wont boot. I will admit, i am an absolute idiot who shouldn't be within a mile of Linux, but I wanted to learn. in other words, i know literally nothing.
Although I don't know if I was doing it right, I don't think I can boot into safe mode, when I tried I got the attached errors. My method was to restart the PC, it was in a state where it was blackscreened but on. I restarted it so that it put me in the menu where you get to like the admin password for the device and what not, and i choose the advanced options for Ubuntu, and choose to boot in the most recent version safe mode. and got the errors. the drivers i attempted to download were installed through the commands "sudo apt install nvidia-driver-550" then the command "sudo ubuntu-drivers install" and then going to additional drivers and clicking "xserver-xorg-video-nouveau" and applying, in that specific order if it matters. after which I restarted, and had all the problems.