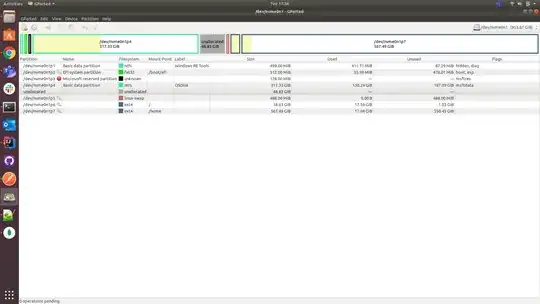
Lately my root partition is running out of space which is causing me problems, and I constantly have to free some space in order to avoid it. After 2-3 days my root partition gets full again. The only solution that i find is to increase the size of my root partition, but as a newbie on Linux systems I am afraid of data loss. My laptop has dual boot of Windows 10 / Ubuntu 18.04. Is there any way that I can use the unallocated space that I created here in order to extend the root partition?
1 Answers
We'll repartition your disk, as requested, but also convert you from a (too small) swap partition, to a /swapfile.
Note: Pay close attention to these instructions.
Make sure that you have a good backup of your important Ubuntu files, as this procedure can corrupt or lose data.
DISABLE CURRENT SWAP PARTITION
sudo swapoff -a
sudo -H gedit /etc/fstab
Comment out the swap line that looks similar to this...
UUID=xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx none swap sw 0 0
Save the file and quit gedit.
REPARTITION
Keep these things in mind:
always start the entire procedure with issuing a swapoff on any mounted swap partitions, and end the entire procedure with issuing a swapon on that same swap partition
a move is done by pointing the mouse pointer at the center of a partition and dragging it left/right with the hand cursor
a resize is done by dragging the left/right side of a partition to the left/right with the directional arrow cursor
if any partition can't be moved/resized graphically, you may have to manually enter the specific required numeric data (don't do this unless I instruct you to)
you begin any move/resize by right-clicking on the partition in the lower pane of the main window, and selecting the desired action from the popup menu, then finishing that action in the new move/resize window
Do the following...
Note: if the procedure doesn't work exactly as I outline, STOP immediately and DO NOT continue.
- boot to a Ubuntu Live DVD/USB, in “Try Ubuntu” mode
- start
gparted - set swapoff on /dev/nvme0n1p5
- delete the /dev/nvme0n1p5 old swap partition
- move /dev/nvme0n1p6 partition all the way left
- resize /dev/nvme0n1p6 right side all the way right
- click the Apply icon
- quit
gpartedand reboot the computer
CREATE /swapfile
Now we'll create a fresh new /swapfile...
Note: Incorrect use of the rm and dd commands can cause data loss. Suggest copy/paste.
In the terminal...
sudo swapoff -a # turn off swap
sudo rm -i /swapfile # remove old /swapfile
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1M count=4096
sudo chmod 600 /swapfile # set proper file protections
sudo mkswap /swapfile # init /swapfile
sudo swapon /swapfile # turn on swap
free -h # confirm xxG RAM and 4G swap
Edit /etc/fstab, using sudo -H gedit /etc/fstab or sudo pico /etc/fstab.
Add the following /swapfile line in /etc/fstab... and confirm no other “swap” lines... use SPACES in this line... confirm NO TABS...
/swapfile none swap sw 0 0
Then reboot and verify operation.
RECOMMENDATION
Reducing the size of the /dev/nvme0n1p7 partition, and creating a new NTFS partition, that can be used for sharing files between Windows and Ubuntu.
- 73,649