I am want to uninstall ubuntu(16.04), from my dual boot system and probably reinstall ubuntu or install kali(dual boot it with windows). I want to allocate more space to the already existing windows. I have 10 partitions and I want to figure out if any of these partitions can be freed(not necessary for windows) so that I can increase the disk space allocated to windows as well as allocate more storage to Kali.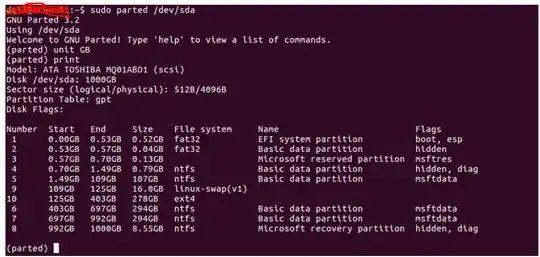
- 23
2 Answers
If you remove partitions /dev/sda9 and /dev/sda10 (swap and Ubuntu), which you might want to do to remove Ubuntu, then you won't be able to just boot into Windows any more because GRUB (the bootloader which should be installed in /dev/sda10) will be gone. If you then re-install Ubuntu, or another Linux, you'll be fine. You'll also be fine (be able to boot into Windows) if you delete /dev/sda9 but leave /dev/sda10 alone.
Currently, in Windows, (C: is probably /dev/sda5) you probably have a D: and E: drives, and that would account for the extra partitions /dev/sda6 and /dev/sda7. You'll have to see what files are there, if you have external backups, and if you still need/want those drives in Windows.
You shouldn't touch the other partitions.
First, you need to figure out what each partition contains. We are only interested in partitions 5, 6 and 7 since 1 is the EFI system partition, 2,3 and 4 are some sort of diagnostic tool for Windows or your laptop or something like that. Not safe to delete in any case and not relevant since they're tiny. Partition 9 in your swap for Ubuntu, 10 is your Ubuntu's root (/) partition (where your Ubuntu is installed) and 8 is Windows' recovery partition. So let's see what the rest are.
First of all, you will need to mount them. Open a terminal and run these commands:
Make the mountpoints. This will create directories
sda5,sda6andsda7.mkdir sda{5,6,7}Mount each partition onto its corresponding directory
for d in sda{5,6,7}; do sudo mount -t ntfs /dev/"$d" $d" doneNow, check the contents of each of them to figure out what they are and which ones you can delete. Just run
ls:ls sda5 ls sda6 ls sda7
Once you know what's what, you can choose to delete and/or resize as desired.
- 104,119