Consider the sequence of numbers  and define the difference
and define the difference  . Now sum the differences and not that all but the first and last terms cancel:
. Now sum the differences and not that all but the first and last terms cancel:

In other words  . It seems obvious that,
. It seems obvious that,

Changing variables:

or as an indefinite integral:

Converse
In other words, the integral of the derivative of a function is the original function. But what of the derivative of the integral? Let,
 where
where  .
.
Here, we assume that all the intervals  in the Riemann sum are equal. To find
in the Riemann sum are equal. To find  we need to add one extra term to the Riemann sum:
we need to add one extra term to the Riemann sum:

 .
.
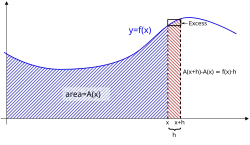 As shown in red, the change in area (∫fdx) of a function is closely related to the value of the function, f(x) at the point where x changes to x+δx
As shown in red, the change in area (∫fdx) of a function is closely related to the value of the function, f(x) at the point where x changes to x+δx
 .
.
Rearrange this to obtain:

The original Planet Physics version still remains on the page as a hidden comment (visible in "edit" mode)

