Introduction:
metric prefixes
| da | h | k | M | G | T | P | E | Z | Y |
| deca | hecto | kilo | mega | giga | tera | peta | exa | zetta | yotta |
| 1E+01 | 1E+02 | 1E+03 | 1E+06 | 1E+09 | 1E+12 | 1E+15 | 1E+18 | 1E+21 | 1E+24 |
|
| d | c | m | µ | n | p | f | a | z | y |
| deci | centi | milli | micro | nano | pico | femto | atto | zepto | yocto |
| 1E-01 | 1E-02 | 1E-03 | 1E-06 | 1E-09 | 1E-12 | 1E-15 | 1E-18 | 1E-21 | 1E-24 |
1. Units_and_Measurement:
The base SI units are mass: kg (kilogram); length: m (meter); time: s (second). [1]
Percent error is 
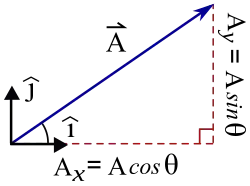
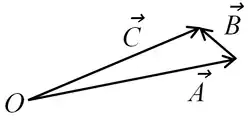
2. Vectors: Vector  involves components (Ax,Ay,Az) and [2] unit vectors.[3] ▭ If
involves components (Ax,Ay,Az) and [2] unit vectors.[3] ▭ If  , then Ax+Bx=Cx, etc, and vector subtraction is defined by
, then Ax+Bx=Cx, etc, and vector subtraction is defined by  .
.
▭ The two-dimensional displacement from the origin is  . The magnitude is
. The magnitude is  . The angle (phase) is
. The angle (phase) is  .
▭ Scalar multiplication
.
▭ Scalar multiplication  ▭ Any vector divided by its magnitude is a unit vector and has unit magnitude:
▭ Any vector divided by its magnitude is a unit vector and has unit magnitude:  where
where  ▭ Dot product
▭ Dot product  and
and  ▭ Cross product
▭ Cross product 
 where
where  is any cyclic permutation of
is any cyclic permutation of  , i.e., (α,β,γ) represents either (x,y,z) or (y,z,x) or (z,x,y).
▭ Cross-product magnitudes obey
, i.e., (α,β,γ) represents either (x,y,z) or (y,z,x) or (z,x,y).
▭ Cross-product magnitudes obey  where
where  is the angle between
is the angle between  and
and  , and
, and  by the right hand rule.
▭ Vector identities
by the right hand rule.
▭ Vector identities  ▭
▭  ▭
▭  ▭
▭  ▭
▭  ▭
▭  [4]
3. Motion_Along_a_Straight_Line:
[5]
▭ Average velocity
[4]
3. Motion_Along_a_Straight_Line:
[5]
▭ Average velocity  (instantaneous velocity)
▭ Acceleration
(instantaneous velocity)
▭ Acceleration  .
▭ WLOG set
.
▭ WLOG set  and
and  if
if  . Then
. Then  , and
, and
 ,
,  [6]
▭ At constant acceleration:
[6]
▭ At constant acceleration:

 .
▭ For free fall, replace
.
▭ For free fall, replace  (positive up) and
(positive up) and  , where
, where  = 9.81 m/s2 at Earth's surface).
4. Motion_in_Two_and_Three_Dimensions:
Instantaneous velocity:
= 9.81 m/s2 at Earth's surface).
4. Motion_in_Two_and_Three_Dimensions:
Instantaneous velocity:  ▭
▭  , where
, where  ▭ Acceleration
▭ Acceleration  , where
, where  .
[7]
▭ Uniform circular motion: position
.
[7]
▭ Uniform circular motion: position  ,
velocity
,
velocity  ,
and acceleration
,
and acceleration  :
:


 Note that if
Note that if  then
then  where
where  .
[8]
▭ Relative motion:
[9]
.
[8]
▭ Relative motion:
[9]
 ,
[10]
5. Newton's_Laws_of_Motion:
[11]
,
[10]
5. Newton's_Laws_of_Motion:
[11] , where
, where  is momentum, [12]
is momentum, [12]  is the sum of all forces This sum needs only include external forces [13]
is the sum of all forces This sum needs only include external forces [13] .[14]
.[14]
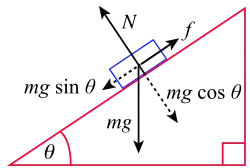
▭ Weight .
▭ normal force[15]
.
▭ normal force[15]  [16]
▭ [17]
[16]
▭ [17] where
where  is the spring constant.
6. Applications_of_Newton's_Laws:
is the spring constant.
6. Applications_of_Newton's_Laws:
 :
:  friction,
friction,  coefficient of (static,kinetic) friction,
coefficient of (static,kinetic) friction,  normal force.
▭ Centripetal force
normal force.
▭ Centripetal force for uniform circular motion. Angular velocity
for uniform circular motion. Angular velocity  is measured in radians per second.
[18]▭ Drag equation
is measured in radians per second.
[18]▭ Drag equation  where
where  Drag coefficient,
Drag coefficient,  mass density,
mass density,  area,
area,  speed. Holds approximately for large Reynold's number[19]
7. Work_and_Kinetic_Energy:
Infinitesimal work[20]
speed. Holds approximately for large Reynold's number[19]
7. Work_and_Kinetic_Energy:
Infinitesimal work[20]  leads to the
path integral
leads to the
path integral  ▭ Work done from A→B by friction
▭ Work done from A→B by friction  gravity
gravity  and spring
and spring  ▭ Work-energy theorem: [21]
▭ Work-energy theorem: [21]  where kinetic energy
where kinetic energy  .
▭ Power
.
▭ Power .
8. Potential_Energy_and_Conservation_of_Energy:
Potential Energy:
.
8. Potential_Energy_and_Conservation_of_Energy:
Potential Energy:  ; PE at
; PE at  WRT
WRT  is
is 
 (gravitational PE Earth's surface.
(gravitational PE Earth's surface.  (ideal spring)
▭ Conservative force:
(ideal spring)
▭ Conservative force:  . In 2D,
. In 2D,  is conservative if and only if
is conservative if and only if  ▭ Mechanical energy is conserved if no non-conservative forces are present:
▭ Mechanical energy is conserved if no non-conservative forces are present:
 9. Linear_Momentum_and_Collisions:
9. Linear_Momentum_and_Collisions:
 is momentum.
▭ Impulse-momentum theorem
is momentum.
▭ Impulse-momentum theorem  .
▭ For 2 particles in 2D
.
▭ For 2 particles in 2D
 where (α,β)=(x,y)
▭ Center of mass:
where (α,β)=(x,y)
▭ Center of mass: 
 , and
, and  ▭
▭  [22]
10. Fixed-Axis_Rotation:
[22]
10. Fixed-Axis_Rotation:
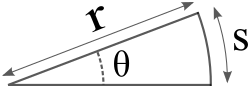

 is angle in radians,
is angle in radians, is angular velocity;
▭
is angular velocity;
▭  is tangential speed. Angular acceleration is
is tangential speed. Angular acceleration is  .
.  is the tangential acceleration.
▭ Constant angular acceleration
is the tangential acceleration.
▭ Constant angular acceleration  is average angular velocity.
▭
is average angular velocity.
▭  ▭
▭ 
 ▭ Total acceleration is centripetal plus tangential:
▭ Total acceleration is centripetal plus tangential:  ▭ Rotational kinetic energy is
▭ Rotational kinetic energy is  where
where  is the Moment of inertia.
▭ parallel axis theorem
is the Moment of inertia.
▭ parallel axis theorem  ▭ Restricting ourselves to fixed axis rotation,
▭ Restricting ourselves to fixed axis rotation,  is the distance from a fixed axis; the sum of torques,
is the distance from a fixed axis; the sum of torques,  requires only one component, summed as
requires only one component, summed as  .
▭ Work done by a torque is
.
▭ Work done by a torque is  . The Work-energy theorem is
. The Work-energy theorem is
 .
▭ Rotational power
.
▭ Rotational power  .
11. Angular_Momentum:
Center of mass
(rolling without slip)
.
11. Angular_Momentum:
Center of mass
(rolling without slip) 

 ▭ Total angular momentum and net torque:
▭ Total angular momentum and net torque: 

 for a single particle.
for a single particle.  ▭ Precession of a top
▭ Precession of a top  12. Static_Equilibrium_and_Elasticity: Equilibrium
12. Static_Equilibrium_and_Elasticity: Equilibrium  Stress = elastic modulus · strain (analogous to Force = k · Δ x )
▭ (Young's , Bulk , Shear) modulus:
Stress = elastic modulus · strain (analogous to Force = k · Δ x )
▭ (Young's , Bulk , Shear) modulus:  13. Gravitation:
Newton's law of gravity
13. Gravitation:
Newton's law of gravity  ▭ Earth's gravity
▭ Earth's gravity  ▭ Gravitational PE beyond Earth
▭ Gravitational PE beyond Earth  ▭ Energy conservation
▭ Energy conservation  ▭ Escape velocity
▭ Escape velocity  ▭ Orbital speed
▭ Orbital speed  ▭ Orbital period
▭ Orbital period  ▭ Energy in circular orbit
▭ Energy in circular orbit  ▭ Conic section
▭ Conic section  ▭ Kepler's third law
▭ Kepler's third law ▭ Schwarzschild radius
▭ Schwarzschild radius  14. Fluid_Mechanics:
Mass density
14. Fluid_Mechanics:
Mass density  ▭ Pressure
▭ Pressure  ▭ Pressure vs depth/height (constant density)
▭ Pressure vs depth/height (constant density) ▭ Absolute vs gauge pressure
▭ Absolute vs gauge pressure  ▭ Pascal's principle:
▭ Pascal's principle:  depends only on depth, not on orientation of A.
▭ Volume flow rate
depends only on depth, not on orientation of A.
▭ Volume flow rate  ▭ Continuity equation
▭ Continuity equation 
 15. Oscillations:
Frequency
15. Oscillations:
Frequency  ,
period
,
period  and
angular frequency
and
angular frequency 
 ▭ Simple harmonic motion
▭ Simple harmonic motion 

 also models the x-component of uniform circular motion.
▭ For
also models the x-component of uniform circular motion.
▭ For  positive:
positive:  ▭ Mass-spring
▭ Mass-spring  ▭ Energy
▭ Energy 
 ▭ Simple pendulum
▭ Simple pendulum  ▭ Physical pendulum
▭ Physical pendulum 
 and
and  measures from pivot to CM.
▭ Torsional pendulum
measures from pivot to CM.
▭ Torsional pendulum 
 ▭ Damped harmonic oscillator
▭ Damped harmonic oscillator 
 where
where  and
and  ▭ [23]Forced harmonic oscillator (MIT wiki!)]
▭ [23]Forced harmonic oscillator (MIT wiki!)] 
 where
where  .
16. Waves:
[24] Wave speed] (phase velocity)
.
16. Waves:
[24] Wave speed] (phase velocity)  where
where  is wavenumber.
▭ Wave and pulse speed of a stretched string
is wavenumber.
▭ Wave and pulse speed of a stretched string  where
where  is tension and
is tension and  is linear mass density.
▭ Speed of a compression wave in a fluid
is linear mass density.
▭ Speed of a compression wave in a fluid  ▭ Periodic travelling wave
▭ Periodic travelling wave  travels in the positive/negative direction. The phase is
travels in the positive/negative direction. The phase is  and the amplitude is
and the amplitude is  .
▭ The resultant of two waves with identical amplitude and frequency
.
▭ The resultant of two waves with identical amplitude and frequency ![{\displaystyle y_{R}(x,t)=\left[2A\cos \left({\tfrac {\phi }{2}}\right)\right]\sin \left(kx-\omega t+{\tfrac {\phi }{2}}\right)}](../../5a6862f6831d0a0f45bd98a9b627d1fc16757308.svg) where
where  is the phase shift.
▭ This wave equation
is the phase shift.
▭ This wave equation  is linear in
is linear in  ▭ Power in a tranverse stretched string wave
▭ Power in a tranverse stretched string wave  .
▭ Intensity of a plane wave
.
▭ Intensity of a plane wave  in a spherical wave.
▭ Standing wave
in a spherical wave.
▭ Standing wave  For symmetric boundary conditions
For symmetric boundary conditions 
 , or equivalently
, or equivalently  where
where  is the fundamental frequency.
17. Sound:
Pressure and displacement fluctuations in a sound wave
is the fundamental frequency.
17. Sound:
Pressure and displacement fluctuations in a sound wave
 and
and  ▭ Speed of sound in a fluid
▭ Speed of sound in a fluid  ,
▭ in a solid
,
▭ in a solid  ,
▭ in an idal gas
,
▭ in an idal gas  ,
▭ in air
,
▭ in air  ▭ Decreasing intensity spherical wave
▭ Decreasing intensity spherical wave  ▭ Sound intensity
▭ Sound intensity  ▭ ...level
▭ ...level  ▭ Resonance tube One end closed:
▭ Resonance tube One end closed:


 ▭ Both ends open:
▭ Both ends open:


 ▭ Beat frequency
▭ Beat frequency  ▭ (nonrelativistic) Doppler effect
▭ (nonrelativistic) Doppler effect  where
where  is the speed of sound,
is the speed of sound,  is the velocity of the source, and
is the velocity of the source, and  is the velocity of the observer.
▭ Angle of shock wave
is the velocity of the observer.
▭ Angle of shock wave  where
where  is the speed of sound,
is the speed of sound,  is the speed of the source, and
is the speed of the source, and  is the Mach number.
is the Mach number.
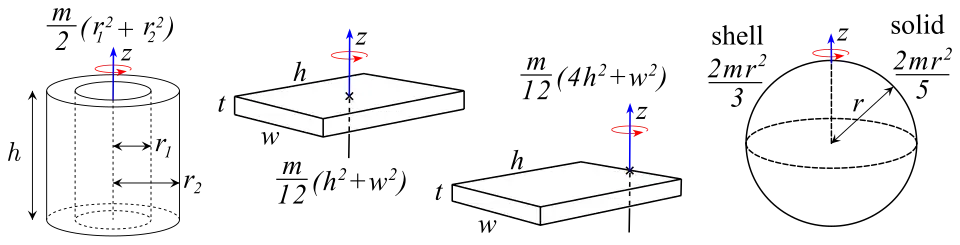 I=∫r2dm for a hoop, disk, cylinder, box, plate, rod, and spherical shell or solid can be found from this figure.
I=∫r2dm for a hoop, disk, cylinder, box, plate, rod, and spherical shell or solid can be found from this figure.
hide this part |
- ↑ [http://wiki.ubc.ca/index.php?title=Uncertainty_and_Error&oldid=81540
- ↑ three orthonormal
- ↑
- ↑
▭
 ▭
▭  ▭ ▭  ▭ ▭ 
- ↑ Delta as difference
 in limit of differential calculus. in limit of differential calculus.
- ↑ , where
 is the average velocity. is the average velocity.
- ↑
▭ Average values:
 , and , and  ▭ Free fall time of flight
▭ Free fall time of flight  ▭ Trajectory
▭ Trajectory ![{\displaystyle y=(\tan \theta _{0})x-\left[{\tfrac {g}{2(v_{0}\cos \theta _{0})^{2}}}\right]x^{2}\,,\,}](../../12c32b4b09920712b8d39704824b2648260bb6d4.svg) ▭ Range ▭ Range 
- ↑ ▭ Tangential and centripetal acceleration
 where where  . .
- ↑
 , ,
- ↑
 , , 
- ↑ Newton's 2nd Law
- ↑
 is mass, and is mass, and
- ↑ because all internal forces cancel by the 3rd law
- ↑ The 1st law is that velocity is constant if the net force is zero.
- ↑ is a component of the contact force by the surface. If the only forces are contact and weight,
- ↑ where
 is the angle of incline. is the angle of incline.
- ↑ Hooke's law
- ↑ ▭ Ideal angle of banked curve:
 for curve of radius for curve of radius  banked at angle banked at angle  . .
- ↑
 , where , where  dynamic viscosity; dynamic viscosity;  characteristic length. ▭ Stokes's law models a sphere of radius characteristic length. ▭ Stokes's law models a sphere of radius  at small Reynold's number: at small Reynold's number:  . .
- ↑ done by force:
- ↑ The work done on a particle is
- ↑ ▭ Rocket equation
 where u is the gas speed WRT the rocket. where u is the gas speed WRT the rocket.
- ↑ [https://scripts.mit.edu/~srayyan/PERwiki/index.php?title=Module_3_--_Damped_and_Driven_Harmonic_Oscillations&oldid=7055
- ↑ [http://wiki.ubc.ca/index.php?title=Waves_and_the_Doppler_Effect&oldid=218637
|






