Inverse-producing extensions of Topological Algebras/Algebra of polynomials
Introduction
A polynomial algebra is a vector space of polynomials, where the coefficients come from the given algebra . The polynomial algebra is an essential tool to construct an algebra extension of in which a given is invertible if it satisfies certain topological invertibility criteria.
Remark: Algebra expansion
In the construction of algebra extension in which a is invertible, the first step is to consider the algebra of polynomials . The following figure shows how the algebra extension is constructed over the polynomial algebra.
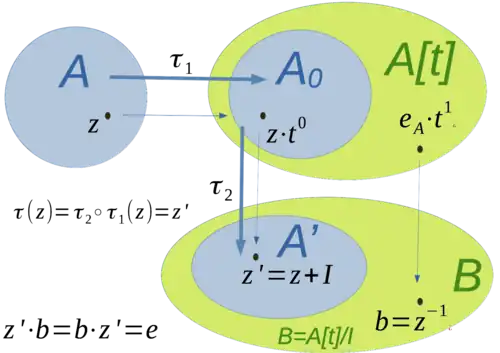
Algebraic closure
We only extend the algebra to contain an additional element , which is to be contained in an algebra extension of . Since multiplication and addition must be completed in , polynomials result from multiplications and with coefficients n, which must be contained as summands as polynomials in the algebra expansion.
Extension of the algebra
This implies the closure of the
- multiplicative linkage of with itself and therefore with must also be in again,
- the arbitrary multiplicative links of with elements from lie again in , i.e. .
- the additive algebraic algebraic closure also eventually requires that additive links from lie again in .
Polynomials with coefficients from the given algebra
Out of this necessity, one considers polynomials with coefficients from as the first step in constructing an algebra expansion in which a can be invertible.
Polynomial algebra
We now consider, for a given topological algebra , the set of polynomials with coefficients in .
and power series with coefficients in algebra .
Degree of polynomials
First of all, polynomials would be more formally notated in the above form with and with would indicate the degree of the polynomial. For the Cauchy product of two polynomials , however, this notation is unsuitable, since in the addition and multiplication two polynomials the handling of the degree entails additional formal overhead, which, however, does not matter for the further considerations of algebra expansions.
Notation for the polynomial algebra
Therefore, polynomials are defined as follows over "finite" sequences , which from an index bound consists only of the zero vector in .
Cauchy product
Given, in general, two polynomials with coefficients from .
Then Cauchy product of is defined as follows:
Page Information
You can display this page as Wiki2Reveal slides
Wiki2Reveal
The Wiki2Reveal slides were created for the Inverse-producing extensions of Topological Algebras' and the Link for the Wiki2Reveal Slides was created with the link generator.
- This page is designed as a PanDocElectron-SLIDE document type.
- Source: Wikiversity https://en.wikiversity.org/wiki/Inverse-producing%20extensions%20of%20Topological%20Algebras/Algebra%20of%20polynomials
- see Wiki2Reveal for the functionality of Wiki2Reveal.