 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
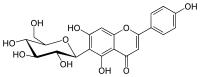
| IUPAC name
6-(β-D-Glucopyranosyl)-4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-6-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
homovitexin, saponaretin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.126.529 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H20O10 | |
| Molar mass | 432.38 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Isovitexin (or homovitexin, saponaretin) is a flavone. the apigenin-6-C-glucoside. In this case, the prefix 'iso' does not imply an isoflavonoid (the position of the B-ring on the C-ring), but the position of the glucoside on the flavone.
Natural occurrence
It can be found in the passion flower, Cannabis, oat and the açaí palm.[1]
Metabolism
Glycosides
Saponarin is the isovitexin-7-O-glucoside.
See also
- Vitexin, the 8-C-glucoside of apigenin
- Isoorientin, the 3'-OH derivative
References
- ↑ "Pharmacological studies of Passiflora sp. and their bioactive compounds"
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.