| Compound of n p/q-gonal antiprisms | |||
|---|---|---|---|
n=2
| |||
| Type | Uniform compound | ||
| Index |
| ||
| Polyhedra | n p/q-gonal antiprisms | ||
| Schläfli symbols (n=2) | ß{2,2p/q} ßr{2,p/q} | ||
| Coxeter diagrams (n=2) | |||
| Faces | 2n {p/q} (unless p/q=2), 2np triangles | ||
| Edges | 4np | ||
| Vertices | 2np | ||
| Symmetry group |
| ||
| Subgroup restricting to one constituent |
| ||
In geometry, a prismatic compound of antiprism is a category of uniform polyhedron compound. Each member of this infinite family of uniform polyhedron compounds is a symmetric arrangement of antiprisms sharing a common axis of rotational symmetry.
Infinite family
This infinite family can be enumerated as follows:
- For each positive integer n≥1 and for each rational number p/q>3/2 (expressed with p and q coprime), there occurs the compound of n p/q-gonal antiprisms, with symmetry group:
- Dnpd if nq is odd
- Dnph if nq is even
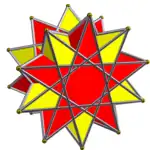
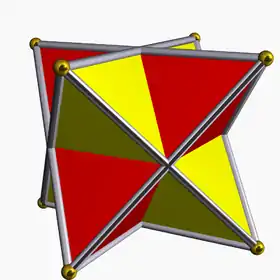
Where p/q=2, the component is the tetrahedron (or dyadic antiprism). In this case, if n=2 then the compound is the stella octangula, with higher symmetry (Oh).
Compounds of two antiprisms
Compounds of two n-antiprisms share their vertices with a 2n-prism, and exist as two alternated set of vertices.
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of an antiprism with n-gonal bases and isosceles triangles are
with k ranging from 0 to 2n−1; if the triangles are equilateral,
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 2 digonal antiprisms (tetrahedra) |
2 triangular antiprisms (octahedra) |
2 square antiprisms |
2 hexagonal antiprisms |
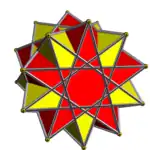
2 pentagrammic crossed antiprism |
Compound of two trapezohedra (duals)
The duals of the prismatic compound of antiprisms are compounds of trapezohedra:
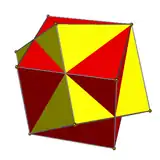 Two cubes (trigonal trapezohedra) |
Compound of three antiprisms
For compounds of three digonal antiprisms, they are rotated 60 degrees, while three triangular antiprisms are rotated 40 degrees.
 |
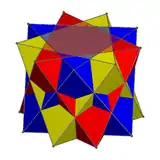 |
| Three tetrahedra | Three octahedra |
|---|
References
- Skilling, John (1976), "Uniform Compounds of Uniform Polyhedra", Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 79 (3): 447–457, doi:10.1017/S0305004100052440, MR 0397554.