 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
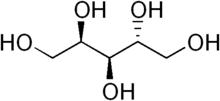
| IUPAC name
D-Arabinitol[2] | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,4R)-Pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol | |
| Other names
(2R,4R)-Pentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentaol (not recommended) Arabitol Lyxitol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.988 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 152.146 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Prismatic crystals |
| Melting point | 103 °C (217 °F; 376 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Arabitol, or arabinitol, is a sugar alcohol. It can be formed by the reduction of either arabinose or lyxose. Some organic acid tests check for the presence of D-arabitol, which may indicate overgrowth of intestinal microbes such as Candida albicans or other yeast/fungus species.[3]
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 789
- ↑ "2-Carb-19".
- ↑ "Candida and Yeast Overgrowth". Archived from the original on 2010-03-02. Retrieved 2010-03-16.
Further reading
- Herman, Anna; Herman, Andrzej Przemysław (15 January 2022). "Could Candida Overgrowth Be Involved in the Pathophysiology of Autism?". Journal of Clinical Medicine. 11 (2): 442. doi:10.3390/jcm11020442. PMC 8778531. PMID 35054136.
External links
 Media related to Arabitol at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Arabitol at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
